Oracle was founded in 1977. While it’s not exactly GE or IBM, which date back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries respectively, it is old enough to be experiencing a fair bit of disruption in its own right. For a good part of its existence, it sold databases to some of the biggest companies in the world. But today, as the market changes and shifts from on-prem data centers to the cloud, how does a company like Oracle make that transition?
Of course, Oracle has been making the shift to the cloud for the last several years, but it would be fair to say that it came late. Plus, it takes more than building some data centers and pushing out some products to change a company the size of Oracle. The company leadership recognizes this, and has been thinking at the highest levels of the organization about how to, from a cultural and business perspective, successfully transform into a cloud company.
To that end, Oracle has opened five innovation hubs over the last several years, with locations in Austin, Texas; Reston, Va.; Burlington, Mass.; Bangalore, India and Santa Monica, Calif. What are these centers hoping to achieve, and how will it extend to the rest of the company the lessons learned? Those are big questions Oracle must answer to make some headway in the cloud market.
Understanding the problem
Oracle seems to understand it has to do something different to change market perception and its flagging market position. Synergy Research, a firm that tracks cloud market share, reports that the company is struggling.
“For cloud infrastructure services (IaaS, PaaS, hosted private cloud services) — Oracle has a 2 percent share,” John Dinsdale, chief analyst and managing director at Synergy told TechCrunch. He added, “It is a top-10 player, but it is nowhere near the scale of the leading cloud providers; and its market share has been steadily eroding.”
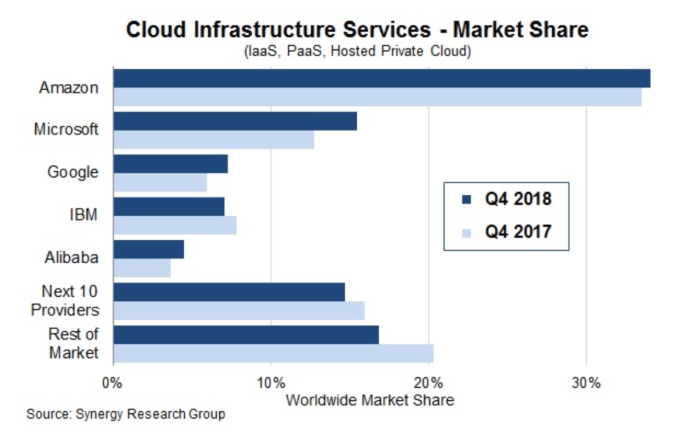
The news is a bit better when it comes SaaS. “Along with SAP, Oracle is one of the leaders in the ERP segment. But enterprise SaaS is much broader than ERP and across all of enterprise SaaS it is the No. 4-ranked provider behind Microsoft, Salesforce and Adobe. Oracle worldwide market share in Q4 was 6 percent,” Dinsdale said.
The company knows that it will take a vast shift to change from an organization that mostly sold software licenses and maintenance agreements. It pushed those hard, sometimes so hard that it left IT pros with a sour taste in their mouths. Today, with the cloud, the selling landscape has changed dramatically to a partnership model. The company knows that it must change, too. The question is, how?
That will take an entirely new approach to product development, sales and marketing; and the innovation hubs have become a kind of laboratory where engineers can experiment with more focused projects, and learn to present their ideas with goal of showing instead of telling customers what they can do.
And the young shall lead
One way to change the culture is to infuse it with fresh-thinking, smart young people, and that’s what Oracle is attempting to do with these centers, where they are hiring youthful engineers, many right out of college, to lead the change with the help of more seasoned Oracle executives.
They are looking for ways to rethink Oracle’s cloud products, to pull the services together into packages of useful tools that helped solve specific business problems, from prescription opioid abuse to predicting avocado yields. The idea isn’t just to have some section of the company where people work on dream projects. They want them to relate to real business problems that results, eventually, in actual sales and measurable results.
Hamza Jahangir, group vice president for the cloud solution hubs at Oracle, says they look for people who want to dig into new solutions, but they want a practical streak in their innovation hub hires. “We don’t want just tinkerers. If the only problem you’re solving is that of your own boredom, that’s not the type of person we are looking for,” he said.
Executive buy-in
The idea of the innovation center actually began with CEO Mark Hurd, according to Jahangir. He had been working for several years to change the nature of the sales force, the one that had a reputation of strong-arming IT pros, with a new generation, by hiring people right out of college with a fresh approach.
Hurd didn’t want to stop with sales, though. He began looking at taking that same idea of hiring younger employees to drive that cultural shift in engineering, too. “About two years ago, Mark challenged us to think about how can we change the customer-facing tech workforce as the business model was moving to the cloud,” Jahangir said.
Hurd gave him some budget to open the first two centers in Austin and Reston and he began experimenting, trying to find the right kinds of employees and projects to work on. The funding came without of a lot of strings or conditions associated with it. Hurd wanted to see what could happen if they unleashed a new generation of workers and gave them a certain amount of freedom to work differently than the traditional way of working at Oracle.
Changing expectations
Jahangir was very frank when it came to assessing customer’s expectations around Oracle moving to the cloud. There has been a lot of skepticism, and part of the reason for the innovation centers was to find practical solutions that could show customers that they actually had modern approaches to computing, given a chance.
The general customer stance has been, “We don’t believe you have anything real, and we need to see true value realized by us before we pay you any money,” he said. That took a fundamental shift to focusing on actual solutions. It started with the premise that the customers shouldn’t believe any of the marketing stuff. Instead, it would show them.
“Don’t bother watching a PowerPoint presentation. Ask us to show you real solutions and use cases where we have solved real material problems — and then we can have a discussion.”
Even chairman and company founder Larry Ellison recognizes the relationship and selling model needed to change as the company moves to the cloud. Jahangir relayed something he said in a recent internal meeting, “In the cloud we are now no longer selling giant monolithic software. Instead we are selling small bites of the apple. The relationship between the vendor and the buyer is becoming more like a consumer model.” That in turn requires a new way of selling and delivering solutions, precisely what they are trying to figure out at the innovation hubs.
Putting the idea to work
Once you have a new way of thinking, you have to put it to work, and as the company has created these various hubs, that has been the approach. As an example, one that isn’t necessarily original, but that puts Oracle features together in a practical way, is the connected patient. The patient wears a Fitbit-like monitor and uses a smart blood pressure cuff and a smart pill box.
The patient can then monitor his or her own health with these tools in a consolidated mobile application that pulls this data together for them using the Internet of Things cloud service, Oracle Mobile Cloud and Oracle Integration Cloud. What’s more, that information gets shared with the patient’s pharmacy and doctor, who can monitor the patient’s health and get warnings when there is a serious issue, such as dangerously high blood pressure.
Another project involved a partnership with Waypoint Robotics, where they demonstrated a robot that worked alongside human workers. The humans interacted with the robots, but the robot moved the goods from workstation to workstation, acting as a quality control agent along the way. If it found defects or problems, it communicated that to the worker via a screen on the side of the unit, and to the cloud. Every interaction between the humans, goods and robot was updated in the Oracle cloud.

Waypoint Robotics robot inspecting iPhones. Information on the display shows it communicating with the Oracle cloud. Photo: Ron Miller
One other project worked with farmers and distributors to help stores stay stocked with avocados, surely as good a Gen Z project as you are likely to find. The tool looks at weather data, historical sales and information coming from sensors at the farm, and it combines all of that data to make predictions about avocado yields, making use of Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse, Oracle Analytics Cloud and other services from the Oracle cloud stack.
Moving beyond the hubs
This type of innovation hub has become popular in recent years as a way to help stave off disruption, and Oracle’s approach is actually in line with this trend. While companies sometimes isolate these innovation hubs to protect them from negativity and naysayers in an organization, leaving them isolated often prevents the lessons learned from being applied to the broader organization at large, essentially defeating the very purpose of creating them in the first place.
Jahangir says that they are attempting to avoid that problem by meeting with others in the company and sharing their learnings and the kinds of metrics that they use in the innovation center to measure success, which might be different from the rest of the company.
He says to put Oracle on the customer agenda, they have to move the conversation from religious battles, as he calls how people support or condemn tech from certain companies. “We have to overcome religious battles and perceptions. I don’t like to fight religion with more religion. We need to step out of that conversation. The best way we have seen for engaging developer community is to show them how to build really cool things, then we can hire developers to do that, and showcase that to the community to show that it’s not just lip service.”
The trick will be doing that, and perhaps the innovation centers will help. As of today, the company is not sharing its cloud revenue, so it’s hard to measure just how well this is helping contribute to the overall success of the company. But Oracle clearly has a lot of work to do to change the perception of the enterprise buyer about its cloud products and services, and to increase its share of the growing cloud pie. It hopes these innovations hubs will lead the way to doing that.
Jahangir recognizes that he has to constantly keep adjusting the approach. “The hub model is still maturing. We are finding and solving new problems where we need new tooling and engagement models in the organization. We are still learning and evolving,” he said.





 Oracle might not be the first company you think of when it comes to cloud computing, but the company has made significant strides in recent years. Today, it announced the bi-annual update to its Oracle Cloud Applications Suite. This is update number 13 for those keeping score at home. The suite includes a range of enterprise software including ERP (think back-office management), HR and CRM/CX…
Oracle might not be the first company you think of when it comes to cloud computing, but the company has made significant strides in recent years. Today, it announced the bi-annual update to its Oracle Cloud Applications Suite. This is update number 13 for those keeping score at home. The suite includes a range of enterprise software including ERP (think back-office management), HR and CRM/CX…