Ten years ago, the vast majority of designers were working in Adobe Photoshop, a powerful tool with fine-tuned controls for almost every kind of image manipulation one could imagine. But it was a tool built for an analog world focused on photos, flyers and print magazines; there were no collaborative features, and much more importantly for designers, there were no other options.
Since then, a handful of major players have stepped up to dominate the market alongside the behemoth, including InVision, Sketch, Figma and Canva.
And with the shift in the way designers fit into organizations and the way design fits into business overall, the design ecosystem is following the same path blazed by enterprise SaaS companies in recent years. Undoubtedly, investors are ready to place their bets in design.
But the question still remains over whether the design industry will follow in the footprints of the sales stack — with Salesforce reigning as king and hundreds of much smaller startup subjects serving at its pleasure — or if it will go the way of the marketing stack, where a lively ecosystem of smaller niche players exist under the umbrella of a handful of major, general-use players.
“Deca-billion-dollar SaaS categories aren’t born everyday,” said InVision CEO Clark Valberg . “From my perspective, the majority of investors are still trying to understand the ontology of the space, while remaining sufficiently aware of its current and future economic impact so as to eagerly secure their foothold. The space is new and important enough to create gold-rush momentum, but evolving at a speed to produce the illusion of micro-categorization, which, in many cases, will ultimately fail to pass the test of time and avoid inevitable consolidation.”
I spoke to several notable players in the design space — Sketch CEO Pieter Omvlee, InVision CEO Clark Valberg, Figma CEO Dylan Field, Adobe Product Director Mark Webster, InVision VP and former VP of Design at Twitter Mike Davidson, Sequoia General Partner Andrew Reed and FirstMark Capital General Partner Amish Jani — and asked them what the fierce competition means for the future of the ecosystem.
But let’s first back up.
Past
Sketch launched in 2010, offering the first viable alternative to Photoshop. Made for design and not photo-editing with a specific focus on UI and UX design, Sketch arrived just as the app craze was picking up serious steam.
A year later, InVision landed in the mix. Rather than focus on the tools designers used, it concentrated on the evolution of design within organizations. With designers consolidating from many specialties to overarching positions like product and user experience designers, and with the screen becoming a primary point of contact between every company and its customers, InVision filled the gap of collaboration with its focus on prototypes.
If designs could look and feel like the real thing — without the resources spent by engineering — to allow executives, product leads and others to weigh in, the time it takes to bring a product to market could be cut significantly, and InVision capitalized on this new efficiency.
In 2012, came Canva, a product that focused primarily on non-designers and folks who need to ‘design’ without all the bells and whistles professionals use. The thesis: no matter which department you work in, you still need design, whether it’s for an internal meeting, an external sales deck, or simply a side project you’re working on in your personal time. Canva, like many tech firms these days, has taken its top-of-funnel approach to the enterprise, giving businesses an opportunity to unify non-designers within the org for their various decks and materials.
In 2016, the industry felt two more big shifts. In the first, Adobe woke up, realized it still had to compete and launched Adobe XD, which allowed designers to collaborate amongst themselves and within the organization, not unlike InVision, complete with prototyping capabilities. The second shift was the introduction of a little company called Figma.
Where Sketch innovated on price, focus and usability, and where InVision helped evolve design’s position within an organization, Figma changed the game with straight-up technology. If Github is Google Drive, Figma is Google Docs. Not only does Figma allow organizations to store and share design files, it actually allows multiple designers to work in the same file at one time. Oh, and it’s all on the web.
In 2018, InVision started to move up stream with the launch of Studio, a design tool meant to take on the likes of Adobe and Sketch and, yes, Figma.
Present
When it comes to design tools in 2019, we have an embarrassment of riches, but the success of these players can’t be fully credited to the products themselves.
A shift in the way businesses think about digital presence has been underway since the early 2000s. In the not-too-distant past, not every company had a website and many that did offered a very basic site without much utility.
In short, designers were needed and valued at digital-first businesses and consumer-facing companies moving toward e-commerce, but very early-stage digital products, or incumbents in traditional industries had a free pass to focus on issues other than design. Remember the original MySpace? Here’s what Amazon looked like when it launched.
In the not-too-distant past, the aesthetic bar for internet design was very, very low. That’s no longer the case.

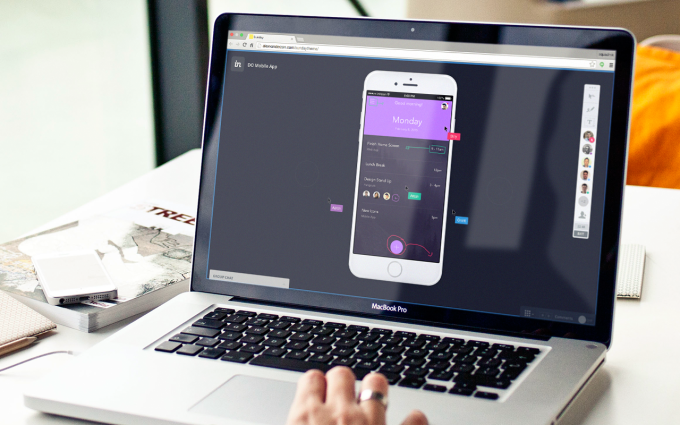 InVision, the platform for creation and collaboration among designers, has today announced the launch of the InVision Fund. Led by CEO Clark Valberg, the company is designating $5 million to invest in startups working in the design space. “The world is giving birth to all of these little design tools meant to make the world of design better,” said Valberg. “We think of…
InVision, the platform for creation and collaboration among designers, has today announced the launch of the InVision Fund. Led by CEO Clark Valberg, the company is designating $5 million to invest in startups working in the design space. “The world is giving birth to all of these little design tools meant to make the world of design better,” said Valberg. “We think of…