Even with all the years of work that have been put into improving how screen-based interfaces work, our experiences with websites, mobile apps and any other interactive service you might use still often come up short: we can’t find what we want, we’re bombarded with exactly what we don’t need or the flow is just buggy in one way or another.
Now, FullStory, one of the startups that’s built a platform to identify when all of the above happens and provide suggestions to publishers for fixing it — it’s obsessed enough with the issue that it went so far as to trademark the phrase “Rage Clicks”, the focus of its mission — is announcing a big round of funding, a sign of its success and ambitions to do more.
The Atlanta-based company has closed a Series D round of $103 million, an oversubscribed round that actually was still growing between me interviewing the company and publishing this story (when we talked last week the figure was $100 million). Permira’s growth fund — which has previously invested in other customer experience startups like Klarna and Nexthink — is leading this round, with previous investors Kleiner Perkins, GV, Stripes, Dell Technologies Capital, Salesforce Ventures and Glynn Capital also participating.
FullStory, which has raised close to $170 million to date, has confirmed that the investment values the company at $1.8 billion.
Scott Voigt, FullStory’s founder and CEO, tells me that FullStory currently has some 3,100 paying customers on its books across verticals like retail, SaaS, finance and travel (customers include Peloton, the Financial Times, VMware and JetBlue), which collectively are on course to rack up more than 15 billion user sessions this year — working out to 1 trillion interactions involving clicks, navigations, highlights, scrolls and frustration signals. It says that annual recurring revenue has to date risen by more than 70% year-on-year.
The plan now will be to continue investing in R&D to bring more real-time intelligence into its products, “and pass those insights on to customers,” and also to “move more aggressively into Europe and Asia Pacific,” he added.
FullStory competes with others like Glassbox and Decibel, although it also claims its tools have more presence on websites than its three biggest competitors combined.
Working across different divisions like product, customer success and marketing, and engineering, FullStory uses machine learning algorithms to analyze how people navigate websites and other digital interfaces.
If approved as part of the “consent gate” you might encounter because of, say, GDPR regulations, it then tracks things like when people are clicking in areas excessively over a short period of time because of delays (the so-called “rage clicks”); or when a click leads nowhere because of, for example, a blip in a piece of JavaScript; or when a person is just scrolling or moving their mouse or cursor or finger in a frustrated (fast) way — again with little or no subsequent activity (or activity from the customer ceasing altogether) resulting from it. It doesn’t use — nor does it have plans to — use eye tracking, or anything like sentiment analysis around data that customers put into, say, customer response windows.
FullStory then packages up the insights that it does collect into data streams that can be used with various visualization tools (having Salesforce as a strategic backer is interesting in this regard, given that it owns Tableau), or spreadsheets, or whatever a customer chooses to put them into. While it doesn’t offer direct remediation (perhaps an area it could tackle in the future), it does offer suggestions for alternative actions to fix whatever problems are arising.
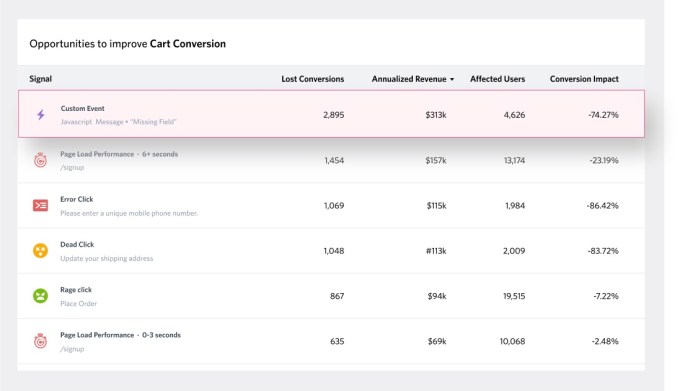
Image Credits: FullStory (opens in a new window)
Part of what has given FullStory a big boost in recent times (this round is by far the biggest fundraise the company has ever done) is the fact that, in today’s world, digital business has become the centerpiece of all business. Because of COVID-19 and the need for social distancing that have taken away some of the traffic of in-person experiences like going to stores, organizations that have natively or built experiences online are seeing unprecedented amounts of traffic; and they are now joined by organizations that have shifted into digital experiences simply to stay in business.
All of that has contributed to a huge amount of content online, and a big shift in mindset to making it better (and in the most urgent of cases, even more basically, simply usable), and that has resulted in the stars aligning for companies like FullStory.
“The category was so nascent to begin with that we had to explain the concept to customers,” Voigt told me of the company’s early days, where selling meant selling would-be customers on to the very idea of digital experience insights. “But digital experience, in the wake of COVID-19, suddenly mattered more than it ever has before, and the continued amount of inbound interest has been afterburner for us.” He noted that demand is increasing among mid-market and enterprise organizations, and something that has also helped FullStory grow is the general movement of talent in the industry.
“Our customers tend to take their tools with them when they change their jobs,” he said. Those tools include FullStory’s analytics.
The evolution of bringing more AI into the world of basically structuring what might otherwise be unstructured data has been a big boost to the world of analytics, and investors are interested in FullStory because of how it’s taken that trend and grown its business on top of it.
“We are very excited to partner with the FullStory team as they continue to expand and build a truly extraordinary technology brand that improves the digital experience for all stakeholders,” said Alex Melamud, who led the transaction on behalf of Permira Growth, in a statement.
“Traditional analytics have been upended by AI- and ML-enabled approaches that can instantly uncover nuanced patterns and anomalies in customer behavior,” said Bruce Chizen, a senior advisor at Permira, in a statement. “Leveraging both structured and unstructured data, FullStory has rapidly established itself as the market and technology leader in DXI and is now the fastest-growing company in the category and the de facto system of record for all digital experience data.” Chizen is joining the FullStory Board with this round.
