Cloud Spanner, Google’s globally distributed relational database service, is getting a bit more distributed today with the launch of a new region and new ways to set up multi-region configurations. The service is also getting a new feature that gives developers deeper insights into their most resource-consuming queries.
With this update, Google is adding to the Cloud Spanner lineup Hong Kong (asia-east2), its newest data center location. With this, Cloud Spanner is now available in 14 out of 18 Google Cloud Platform (GCP) regions, including seven the company added this year alone. The plan is to bring Cloud Spanner to every new GCP region as they come online.
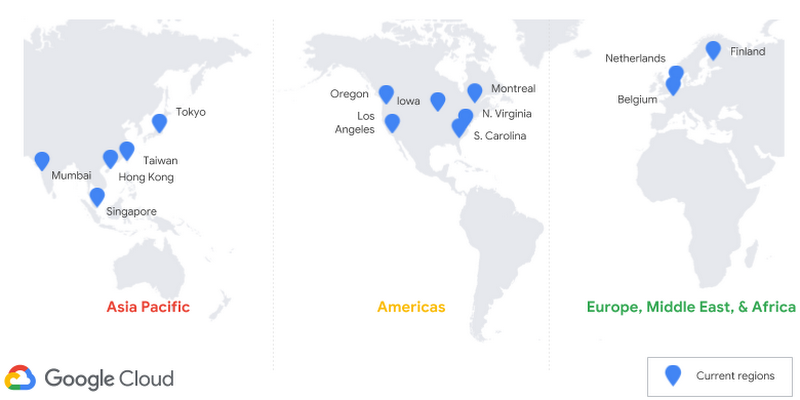
The other new region-related news is the launch of two new configurations for multi-region coverage. One, called eur3, focuses on the European Union, and is obviously meant for users there who mostly serve a local customer base. The other is called nam6 and focuses on North America, with coverage across both costs and the middle of the country, using data centers in Oregon, Los Angeles, South Carolina and Iowa. Previously, the service only offered a North American configuration with three regions and a global configuration with three data centers spread across North America, Europe and Asia.
While Cloud Spanner is obviously meant for global deployments, these new configurations are great for users who only need to serve certain markets.
As far as the new query features are concerned, Cloud Spanner is now making it easier for developers to view, inspect and debug queries. The idea here is to give developers better visibility into their most frequent and expensive queries (and maybe make them less expensive in the process).
In addition to the Cloud Spanner news, Google Cloud today announced that its Cloud Dataproc Hadoop and Spark service now supports the R language, in addition to Python 3.7 support on App Engine.