
 Operators are a software framework that extends Kubernetes API and enables application deployment and management through the control plane. For such complex technologies as databases, Operators play a crucial role by automating deployment and day-to-day operations. At Percona we have the following production-ready and enterprise-grade Kubernetes Operators for databases:
Operators are a software framework that extends Kubernetes API and enables application deployment and management through the control plane. For such complex technologies as databases, Operators play a crucial role by automating deployment and day-to-day operations. At Percona we have the following production-ready and enterprise-grade Kubernetes Operators for databases:
- Percona Distribution for MySQL Operator
- Leverage Percona XtraDB Cluster to deploy a highly reliable MySQL database with synchronous replication based on Galera.
- Percona Distribution for MongoDB Operator
- Deploy scalable MongoDB clusters and leverage enterprise features of Percona Server for MongoDB.
- Percona Distribution for PostgreSQL Operator
- Deploy and manage PostgreSQL clusters on K8S.
Today we are glad to announce an alpha version of our new Operator for MySQL. In this blog post, we are going to answer some frequently asked questions.
Why the New Operator?
As mentioned above, our existing operator for MySQL is based on the Percona XtraDB Cluster (PXC). It is feature-rich and provides virtually-synchronous replication by utilizing Galera Write-Sets. Sync replication ensures data consistency and proved itself useful for critical applications, especially on Kubernetes.
But there are two things that we want to address:
- Our community and customers let us know that there are numerous use cases where asynchronous replication would be a more suitable solution for MySQL on Kubernetes.
- Support Group Replication (GR) – a native way to provide synchronous replication in MySQL without the need to use Galera.
We heard you! That is why our new Operator is going to run Percona Server for MySQL (PS) and provide both regular asynchronous (with semi-sync support) and virtually-synchronous replication based on GR.
What Is the Name of the New Operator?
We will have two Operators for MySQL and follow the same naming as we have for Distributions:
- Percona Distribution for MySQL Operator – PXC (Existing Operator)
- Percona Distribution for MySQL Operator – PS (Percona Server for MySQL)
Is It the Successor of the Existing Operator for MySQL?
Not in the short run. We want to provide our users MySQL clusters on Kubernetes with three replication capabilities:
- Percona XtraDB Cluster
- Group Replication
- Regular asynchronous replication with semi-sync support
Will I Be Able to Switch From One Operator to Another?
We are going to provide instructions and tools for migrations through replication or backup and restore. As the underlying implementation is totally different there is no direct, automated path to switch available.
Can I Use the New Operator Now?
Yes, but please remember that it is an alpha version and we do not recommend it for production workloads.
Our Operator is licensed under Apache 2.0 and can be found in the percona-server-mysql-operator repository on GitHub.
To learn more about our operator please see the documentation.
Quick Deploy
Run these two commands to spin up a MySQL cluster with 3 nodes with asynchronous replication:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/percona/percona-server-mysql-operator/main/deploy/bundle.yaml $ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/percona/percona-server-mysql-operator/main/deploy/cr.yaml
In a couple of minutes, the cluster is going to be up and running. Verify:
$ kubectl get ps NAME MYSQL ORCHESTRATOR AGE cluster1 ready ready 6m16s $ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cluster1-mysql-0 1/1 Running 0 6m27s cluster1-mysql-1 1/1 Running 1 5m11s cluster1-mysql-2 1/1 Running 1 3m36s cluster1-orc-0 2/2 Running 0 6m27s percona-server-for-mysql-operator-c8f8dbccb-q7lbr 1/1 Running 0 9m31s
Connect to the Cluster
First, you need to get the root user password, which was automatically generated by the Operator. By default system users’ passwords are stored in cluster1-secrets Secret resource:
$ kubectl get secrets cluster1-secrets -o yaml | grep root | awk '{print $2}' | base64 --decode
Start another container with a MySQL client in it:
$ kubectl run -i --rm --tty percona-client --image=percona:8.0 --restart=Never -- bash -il
Connect to a primary node of our MySQL cluster from this container:
$ mysql -h cluster1-mysql-primary -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 138 Server version: 8.0.25-15 Percona Server (GPL), Release 15, Revision a558ec2 Copyright (c) 2009-2021 Percona LLC and/or its affiliates Copyright (c) 2000, 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql>
Consult the documentation to learn more about other operational capabilities and options.
What Is Currently Supported?
The following functionality is available in the Operator:
- Deploy asynchronous and semi-sync replication MySQL clusters with Orchestrator on top of it
- Expose clusters with regular Kubernetes Services
- Monitor the cluster with Percona Monitoring and Management
- Customize MySQL configuration
When Will It Be GA? What Is Going to Be Included?
Our goal is to release the GA version late in Q2 2022. We plan to include the following:
- Support for both sync and async replication
- Backups and restores, proxies integration
- Certifications on various Kubernetes platforms and flavors
- Deploy and manage MySQL Clusters with PMM DBaaS
Call for Action
Percona Distribution for MySQL Operator – PS just hatched and your feedback is highly appreciated.
- To report a bug use jira.percona.com and create the bug in K8SPS project.
- For general questions and sharing your thoughts, we have a community forum or Discord where we chat about open source, databases, Kubernetes, and many more.
- Pull requests are as usual welcome at percona-server-mysql-operator repository. See the CONTRIBUTING.md file for details.
Open a bug or create a Pull Request for a chance to get awesome Percona Swag!

 The cloud-native landscape matures every day, and new great tools and products continue to appear. We are starting a series of blog posts that are going to focus on new tools in the container and cloud-native world, and provide a holistic view through the prism of Percona products.
The cloud-native landscape matures every day, and new great tools and products continue to appear. We are starting a series of blog posts that are going to focus on new tools in the container and cloud-native world, and provide a holistic view through the prism of Percona products. Description: CPU and memory resources should have a limit set for every container to prevent resource exhaustion. This control identifies all the Pods without resource limit definition.
Namespace default
Deployment - percona-server-mongodb-operator
StatefulSet - my-cluster-name-cfg
StatefulSet - my-cluster-name-rs0
Summary - Passed:3 Excluded:0 Failed:3 Total:6
Remediation: Define LimitRange and ResourceQuota policies to limit resource usage for namespaces or nodes.
Description: CPU and memory resources should have a limit set for every container to prevent resource exhaustion. This control identifies all the Pods without resource limit definition.
Namespace default
Deployment - percona-server-mongodb-operator
StatefulSet - my-cluster-name-cfg
StatefulSet - my-cluster-name-rs0
Summary - Passed:3 Excluded:0 Failed:3 Total:6
Remediation: Define LimitRange and ResourceQuota policies to limit resource usage for namespaces or nodes.
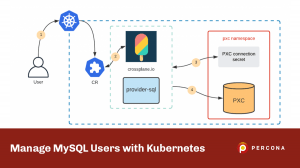 Quite a common request that we receive from the community and customers is to provide a way to manage database users with Operators – both MongoDB and MySQL. Even though we see it as an interesting task, our Operators are mainly a tool to simplify the deployment and management of our software on Kubernetes. Our goal is to provide the database cluster which is ready to host mission-critical applications and deployed with the best practices.
Quite a common request that we receive from the community and customers is to provide a way to manage database users with Operators – both MongoDB and MySQL. Even though we see it as an interesting task, our Operators are mainly a tool to simplify the deployment and management of our software on Kubernetes. Our goal is to provide the database cluster which is ready to host mission-critical applications and deployed with the best practices.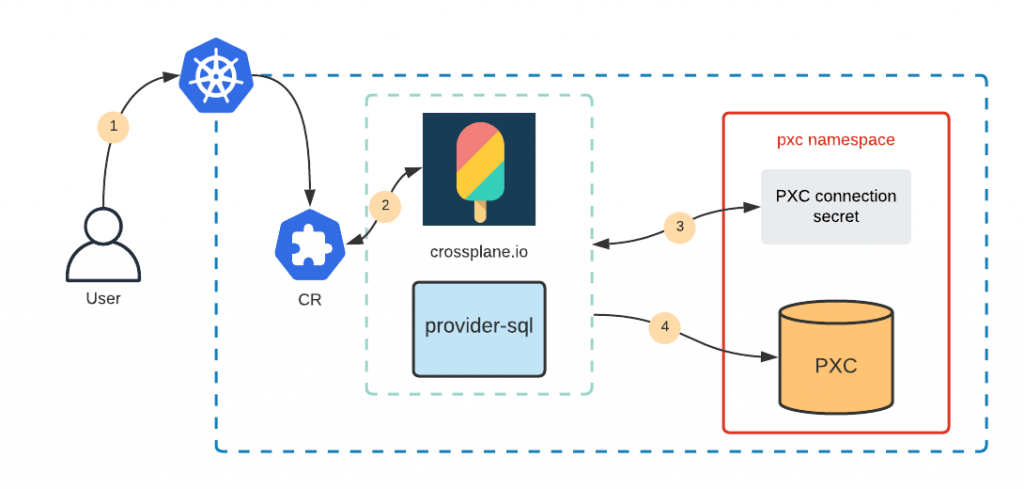

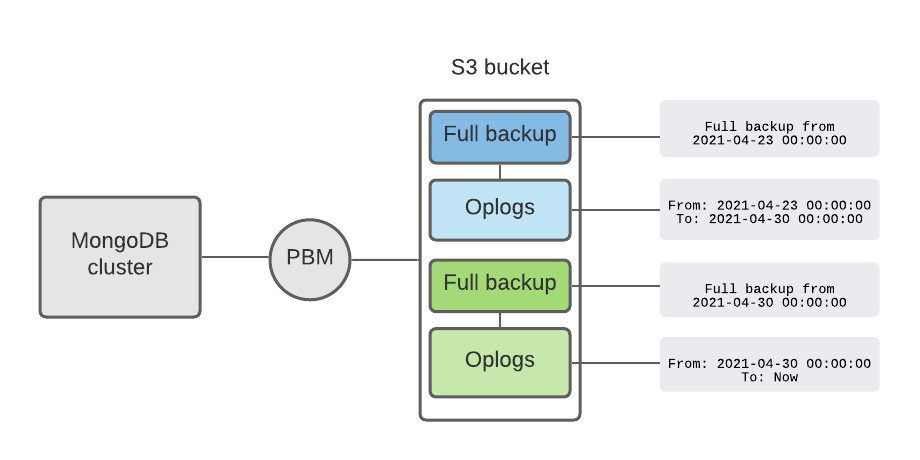
 Running MongoDB in Kubernetes with Percona Operator is not only simple but also by design provides a highly available MongoDB cluster suitable for mission-critical applications. In the latest
Running MongoDB in Kubernetes with Percona Operator is not only simple but also by design provides a highly available MongoDB cluster suitable for mission-critical applications. In the latest 

 Percona Kubernetes Operators
Percona Kubernetes Operators




 It is no secret that compute and storage costs are the main drivers of cloud bills. Migration of data from the legacy data center to the cloud looks appealing at first as it significantly reduces capital expense (CapEx) and keeps operational expenses (OpEx) under control. But once you see the bill, the lift and shift project does not look that promising anymore. See Percona’s recent
It is no secret that compute and storage costs are the main drivers of cloud bills. Migration of data from the legacy data center to the cloud looks appealing at first as it significantly reduces capital expense (CapEx) and keeps operational expenses (OpEx) under control. But once you see the bill, the lift and shift project does not look that promising anymore. See Percona’s recent 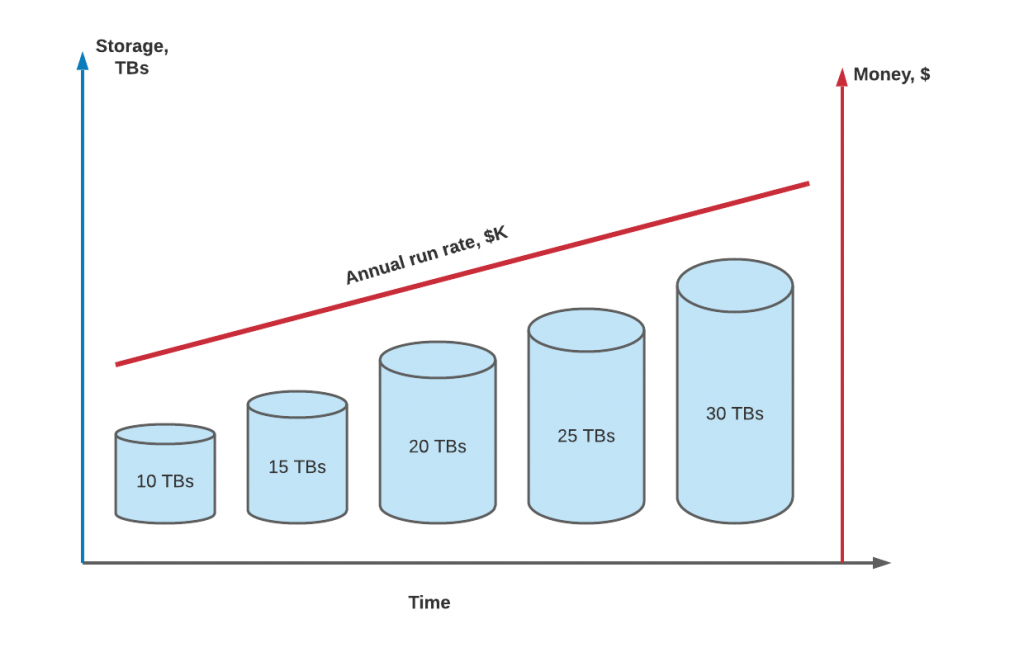

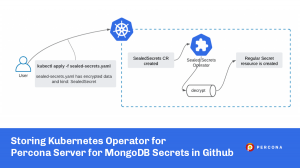 More and more companies are adopting
More and more companies are adopting 
